Define the error function on the whole complex plane by:
where the path is the line segment connecting
and
. Error function is a holomorphic function on
, with an essential singularity at
, now, it is natural to ask what is its asymptotic behavior near the singularity?
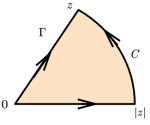
To do the evaluation, by Cauchy’s integral theorem, we can write this integral as
where is an arc coming from the circle centered at the origin with radius
, traveling from
to
, see the following figure :
Now, the first term in the RHS is the real error function, which tends to 1 as goes to
, we will focus on the second term in RHS.
By integration by parts:
By doing this process over and over again, we will obtain a power series in terms of . Indeed, we need to check whether the redundant term tends to zero.
The module of the redundant term is
hence which indeed tends to zero as goes to infinity. Now, to sum up, we have an asymptotic expansion of
at
: